States and Capitals of India – 2025
Posted on : 27 March, 2025 2:32 pm
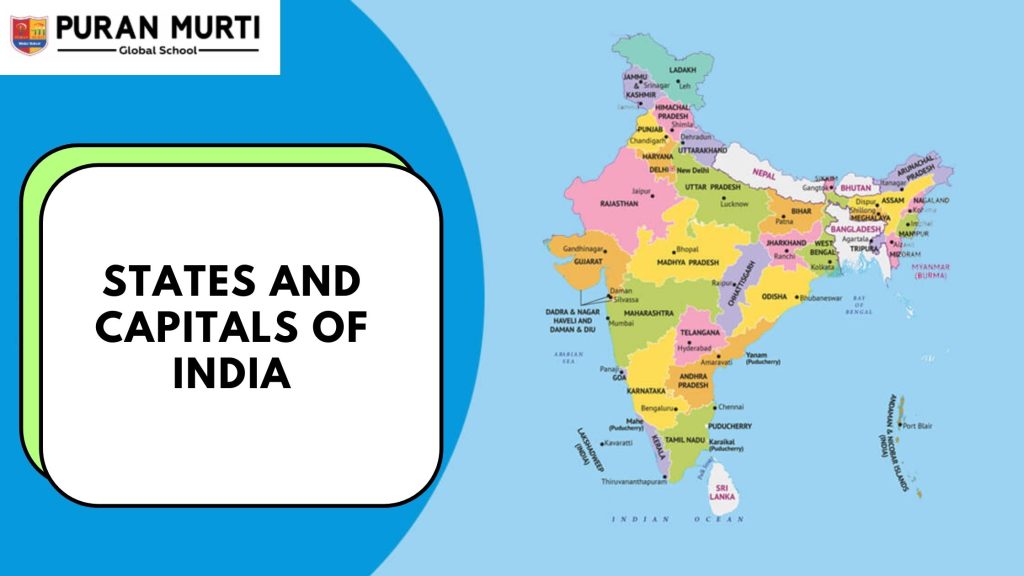
Indian States and capitals
India, being a diverse country, has 28 states and 8 Union Territories, each with a different cultural, geographical, and historical importance. It is imperative to know the Indian States and Capitals in order to understand the political landscape of the country, regional administration, and heritage. This article presents a comprehensive report on India’s states, capitals, and significance.
India is carved out of states, each having a state capital, which also serves as the political, administrative, and many times cultural capital. A full list of Indian states and their capitals follows below:
States and Capitals of 2025
India has 28 states here’s a list of Indian states and capitals :
- Andhra Pradesh – Amaravati
- Arunachal Pradesh – Itanagar
- Assam – Dispur
- Bihar – Patna
- Chhattisgarh – Raipur
- Goa – Panaji
- Gujarat – Gandhinagar
- Haryana – Chandigarh
- Himachal Pradesh – Shimla
- Jharkhand – Ranchi
- Karnataka – Bengaluru
- Kerala – Thiruvananthapuram
- Madhya Pradesh – Bhopal
- Maharashtra – Mumbai
- Manipur – Imphal
- Meghalaya – Shillong
- Mizoram – Aizawl
- Nagaland – Kohima
- Odisha – Bhubaneswar
- Punjab – Chandigarh
- Rajasthan – Jaipur
- Sikkim – Gangtok
- Tamil Nadu – Chennai
- Telangana – Hyderabad
- Tripura – Agartala
- Uttar Pradesh – Lucknow
- Uttarakhand – Dehradun
- West Bengal – Kolkata
Additionally, Delhi serves as the National Capital Territory (NCT) and is also the capital of India.
Indian States and Their Capitals – Regional Overview
Northern States
- Jammu and Kashmir – Srinagar (Summer), Jammu (Winter)
Known for its stunning landscapes and valleys. - Himachal Pradesh – Shimla
Famous for picturesque hill stations and adventure sports. - Punjab – Chandigarh
Rich in culture, music, and cuisine. - Haryana – Chandigarh
Major agricultural state with vibrant festivals. - Uttarakhand – Dehradun
Known for temples and scenic beauty. - Uttar Pradesh – Lucknow
Home to the iconic Taj Mahal and rich heritage.
Eastern States
- Bihar – Patna
Known for ancient monuments and festivals. - Jharkhand – Ranchi
Rich in mineral resources and natural beauty. - West Bengal – Kolkata
Major cultural hub with historic significance. - Odisha – Bhubaneswar
Famous for ancient temples and festivals.
North-Eastern States
- Assam – Dispur
Known for tea gardens and biodiversity. - Arunachal Pradesh – Itanagar
Features lush green landscapes and tribal culture. - Manipur – Imphal
Renowned for its unique culture and festivals. - Meghalaya – Shillong
Famous for its high rainfall and scenic views. - Mizoram – Aizawl
Known for its picturesque hills and tribal culture. - Nagaland – Kohima
Rich in traditional culture and festivals. - Tripura – Agartala
Known for its historic temples and natural beauty. - Sikkim – Gangtok
Famous for its stunning landscapes and monasteries.
Western States
- Rajasthan – Jaipur
Known for its historic forts and vibrant culture. - Gujarat – Gandhinagar
Famous for its diverse culture and economic growth. - Maharashtra – Mumbai
India’s financial capital with a rich cultural heritage. - Goa – Panaji
Known for its beaches and nightlife.
Central States
- Madhya Pradesh – Bhopal
Rich in historical monuments and wildlife. - Chhattisgarh – Raipur
Known for its forests and tribal culture.
Southern States
- Karnataka – Bengaluru
Major IT hub with rich cultural traditions. - Kerala – Thiruvananthapuram
Famous for its backwaters and Ayurvedic treatments. - Tamil Nadu – Chennai
Known for its rich history, temples, and cuisine. - Andhra Pradesh – Amaravati
Known for its historical landmarks and cultural festivals. - Telangana – Hyderabad
Large IT and cultural hub with a rich past.
Importance of Knowing Indian States and Capitals
Knowing the Indian States and their capitals is important for various reasons:
- Educational Purpose: It is an integral part of geography studies, particularly for students who are going to appear in competitive exams such as UPSC and state board exams.
- Travel and Exploration: Traveling in India involves awareness of its states and capitals since it makes travel more enjoyable by facilitating tourists in navigating and understanding the diversity of the country.
- Administrative and Governance Insight: Knowing state capitals is useful in understanding how the Indian political system works. It makes it clear where major decisions are taken and where local governments are located.
How many states in India and their capitals 2025
India consists of 28 states. It also consists of 8 Union Territories. Discover the detailed list of Indian states and capitals, their history, and the importance of their establishment. Understand the Union Territories and their capitals, and have fun with our interactive quiz.
list of 29 states of India and Capitals of India – History
The concept of the States and Capitals of India gained roots in the Indian struggle for freedom. When the day of India being declared free approached, the independent kingdoms that made up the Indian sub-continent entered into a treaty to join princely ruled states together and establish one independent country with shared ethos and objectives. And so, the States and Capitals of India became part of a secular, sovereign republic that embraced democracy and the constitution. On independence day, there were 552 princely states in the country. New lines have been drawn from time to time to mark off the Indian states and their capitals on the basis of shared language or regional identities. The current States and Capitals of India bear this rich history and diversity. The States and Capitals of India are an example of how the country developed and evolved.
States and Capitals of India – 2025
India possesses a rich past, distinctive demography, and diverse culture, attire, languages and celebrations. A state is a sub-division of an Indian constituency and possesses its own government. It is the administrative division of the elected government which enjoys the authority to make its laws. Every Indian state and capitals possesses its Legislative Assembly headed by the Chief Minister for administration. The Governor is the state’s representative of the President.
Union territories are small administrative units which are ruled by the union and administered directly by the central government. A Lieutenant Governor is appointed to it as an administrator. Union Territories have no representation in the Rajya Sabha except for Delhi and Puducherry. India’s official capital, New Delhi is also a union territory.
Here are the 9 union territories of india in 2025
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands – Port Blair
- Daman & Diu – Daman
- Dadra & Nagar Haveli – Daman
- Puducherry – Puducherry
- Delhi – New Delhi
- Jammu & Kashmir – Srinagar (Summer), Jammu (Winter)
- Lakshadweep – Kavaratti
- Chandigarh – Chandigarh
- Ladakh – Leh
How Many Total States are there in India
There are a total of 28 states and 8 Union territories of India. Every state and territory has a specific culture, language, and form of governance, making India so diverse.
The Emergence of Indian states and capitals
There were 14 states and 6 union territories in 1956. These numbered 29 states and 7 union territories in 2014. As of 2025, there are 28 states and 9 Union Territories. The states and union territories are further divided into districts. The states were originally divided on a linguistic basis, but among the new states, most have a common language. For example, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh share the official language of Telugu. Jharkhand was carved out of Bihar and has several languages and cultures in common with the state. Uttarakhand was carved out of Uttar Pradesh, and together with Madhya Pradesh and Delhi, their state language is Hindi.
Articles 2,3, and 4 of the Indian Constitution provide for the formation of new states. Most recently, Jammu and Kashmir were divided into new union territories, having Srinagar in Summer and Jammu in Winter as the capital.
28 Indian States and Union Territories of India
Punjab and Haryana states of India and the Union Territory of Chandigarh are both sharing Chandigarh as their common capital. Telangana and Andhra Pradesh shared Hyderabad as their common capital until the election of Amravati as Andhra Pradesh’s official state capital.
The aim of Indian states and capital is to form smaller administrative units for self-rule. Therefore, every state has its own laws, their government, and law and order machinery.
Indian states and capitals
- Andhra Pradesh: In south-eastern India, Andhra Pradesh boasts diverse culture, rich history, and lively cuisine. Amaravati and Visakhapatnam are the major cities. Famous for ancient temples such as Tirumala Venkateswara and landscapes like the Eastern Ghats.
- Arunachal Pradesh: Arunachal Pradesh in Northeast India is famous for breathtaking natural scenery and tribal societies. Tawang Monastery and Ziro Valley’s scenic beauty surrounded by dense forests and the Himalayas are the highlights.
- Assam: Assam in northeast India is famous for tea gardens and colorful festivals. Kaziranga National Park, where the one-horned rhinoceros resides, and Bihu festival highlight its rich flora and fauna and culture.
- Bihar:Bihar, eastern India, is a historic center with ancient universities such as Nalanda and Bodh Gaya, the birthplace of Buddhism. Its rich traditions and languages are a testament to its cultural richness.
- Chhattisgarh: Chhattisgarh in central India is famous for tribal culture, dense forests, and natural resources. Places of interest are Chitrakote Falls and Hundru Falls, with rich local arts and crafts.
- Goa: Goa, the west coast, is renowned for beaches, nightlife, and Portuguese culture. Beach parties, old churches, and the laid-back tropical vibe are popular among tourists.
- Gujarat: Gujarat, the west of India, has a rich culture, historical landmarks, and economic development. Attractions include Asiatic lions of Gir National Park and the salt desert of the Rann of Kutch.
- Haryana: Haryana, close to Delhi, is famous for its agriculture and economic development. Main places are Kurukshetra and Gurgaon, where traditional life meets contemporary city life.
- Himachal Pradesh: Himalayan Himachal Pradesh, in the north, is characterized by scenic vistas, such as Shimla and Manali. Famous for white-topped peaks, green valleys, and tranquil monasteries, it is a destination round the year.
- Jharkhand: Jharkhand, eastern India, is rich in natural resources and cultural diversity. It features dense forests, waterfalls, and vibrant festivals reflecting its cultural richness.
- Karnataka: Karnataka, southern India, is known for Bengaluru’s IT sector and historic sites like Hampi. It offers a diverse landscape, including coastal regions, forests, and hill stations.
- Kerala: Kerala, “God’s Own Country,” is renowned for backwaters, green landscapes, and peaceful beaches. A few of the attractions are Ayurveda, Onam festival, and cultural syncretism.
- Madhya Pradesh: Central Madhya Pradesh has ancient monuments such as Khajuraho temples and Sanchi Stupa. The state has varied landscapes, rock art, and abundant cultural heritage.
- Maharashtra: Western India’s Maharashtra has Mumbai, the financial hub. Sightseeing includes ancient forts, lovely beaches, and festivities such as Ganesh Chaturthi and Diwali.
- Manipur: Manipur’s northeastern region is rich in culture and natural beauty. Places of interest are picturesque scenery, Manipuri dance, and Yaoshang festivities.
- Meghalaya: Meghalaya in eastern India boasts rolling hills, picturesque waterfalls, and root bridges made from living trees. Shillong, the capital, enjoys comfortable weather and dynamic cultural landscapes.
- Mizoram: Mizoram, north-eastern India, is recognized for its rolling hills, scenic beauty, and rich tribal culture. Chapchar Kut festival and distinctive crafts are major cultural attractions.
- Nagaland: Nagaland, north-east India, is renowned for tribal culture and festivals such as Hornbill Festival. It has rolling hills, forests, and rich festival and craft traditions.
- Odisha: Odisha, the eastern coast, is famous for ancient temples such as Jagannath Temple and scenic beaches. The major cultural features are classical Odissi dance and the festival of Rath Yatra.
- Punjab: Punjab, northern India, has a great cultural heritage with attractions such as the Golden Temple. Famous for Bhangra dance, productivity in agriculture, and lively festivals.
- Rajasthan: Rajasthan, northwestern India, is renowned for desert scenery, impressive forts, and rich culture. Jaipur and Udaipur cities, rich festivals, and traditional arts represent the state.
- Sikkim: Sikkim, eastern Himalayas, is known for its natural grandeur and bio-diversity. Kanchenjunga and colorful monasteries are the attractions as it has its own cultural identity and eco-tourism.
- Tamil Nadu: Tamil Nadu, south India, is famous for ancient temples, classical dance, and unique cuisine. Top spots are Madurai temples, Chennai beaches, and hill resorts such as Ooty.
- Telangana: Telangana, created in 2014, is famed for historical and cultural depth. Hyderabad boasts sites such as Charminar, and local food ranges from Hyderabadi Biryani.
- Tripura: Tripura, eastern India, is known for tribal culture and scenic beauty. Destinations include Ujjayanta Palace, green landscapes, and colorfully traditional celebrations.
- Uttar Pradesh: Uttar Pradesh, northern India, is a cultural center with spots such as the Taj Mahal and the ghats of Varanasi. Its abundant heritage and rich diversity of tradition extend to large cities and ancient sites.
- Uttarakhand: Uttarakhand, north India, is marked by Himalayan scenery and pilgrimage places. Famous spots are Nainital, Rishikesh, and Char Dham temples, which provide space for yoga and adventure sports.
- West Bengal: West Bengal, east India, is famous for cultural heritage, ranging from literature and art to others. Its capital, Kolkata, has historic landmarks and thriving cultural events, from Sunderbans to the Himalayas.